The integration of advanced technologies like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. These tools help professionals design smarter cities, optimize construction projects, and manage assets effectively. While BIM software is well-known for its ability to create detailed 3D models of buildings and infrastructure, ArcGIS, a leading GIS platform, focuses on geospatial analysis and mapping.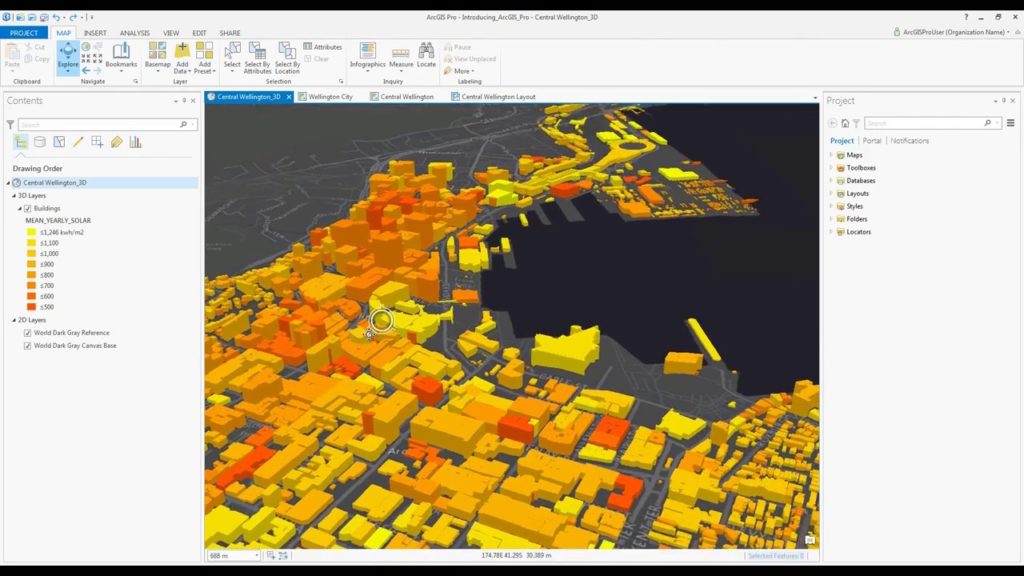
What Is ArcGIS?
ArcGIS, developed by Esri, is one of the most powerful tools for GIS applications. At its core, ArcGIS allows users to create, analyze, and visualize spatial data in a way that provides critical insights for decision-making. Here are its key features:
- Mapping and Visualization: ArcGIS excels at creating detailed maps that integrate various data layers.
- Spatial Analysis: It enables professionals to analyze geographical patterns, relationships, and trends.
- Data Management: The platform supports extensive datasets, including geospatial, demographic, and environmental data.
- 3D Visualization: ArcGIS has features for creating 3D visualizations, particularly useful in urban planning and infrastructure development.
ArcGIS is widely used across industries like urban planning, transportation, environmental science, and disaster management. It provides a spatial context that is indispensable for projects requiring geographical analysis.
What Is BIM Software?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) software is a digital process that creates and manages information about a building or infrastructure project throughout its lifecycle. BIM tools, such as Autodesk Revit and Navisworks, are essential for AEC professionals aiming to design, construct, and manage physical structures effectively.
Key characteristics of BIM software include:
- 3D Modeling: The core functionality of BIM software is its ability to create detailed, information-rich 3D models of buildings.
- Data Integration: BIM integrates data from various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors.
- Collaboration Tools: It enables real-time collaboration, ensuring all project participants are aligned.
- Lifecycle Management: From the design phase to construction and maintenance, BIM manages all aspects of a structure’s lifecycle.
BIM tools are tailored for intricate building designs, making them indispensable for structural detailing, simulations, and cost estimation.
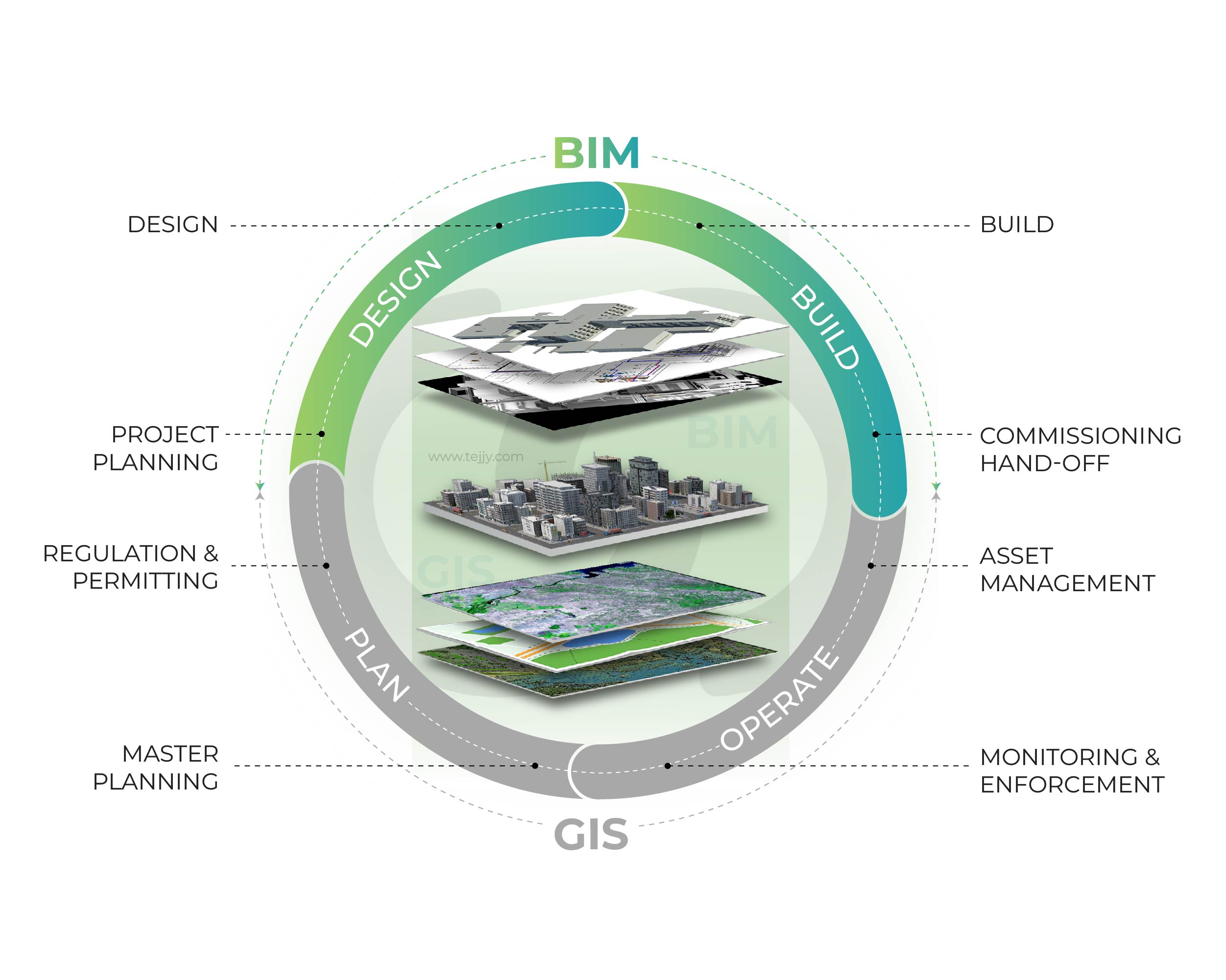
Comparing ArcGIS and BIM Software
Does ArcGIS Function as a BIM Tool?
ArcGIS and BIM software share certain overlapping functionalities, but their core purposes differ significantly. To answer the question, “Is ArcGIS a BIM software?”, it’s essential to delve into what each system is designed to do.
While BIM tools like Autodesk Revit focus on creating detailed 3D models of physical structures, ArcGIS is fundamentally about mapping and analyzing spatial data. Here’s a direct comparison of their key functionalities:
| Feature | ArcGIS | BIM Software |
|---|---|---|
| Core Purpose | Spatial data mapping and analysis | Building design and lifecycle management |
| Data Type | Geographic data (rivers, terrains, etc.) | Structural data (walls, beams, HVAC) |
| 3D Capabilities | Limited to spatial visualizations | Detailed building and infrastructure models |
| Collaboration | Shares geospatial data across teams | Manages design workflows among stakeholders |
While ArcGIS offers some BIM-like features, such as 3D visualizations, it is not a BIM tool in the traditional sense. Instead, ArcGIS complements BIM workflows by adding geospatial insights that BIM tools cannot natively provide.
Can ArcGIS Be Used in BIM Workflows?
ArcGIS is increasingly used in conjunction with BIM to bridge the gap between geospatial data and building design. It excels in providing a broader environmental and locational context that enhances BIM projects. Examples of how ArcGIS integrates into BIM workflows include:
- Site Analysis: ArcGIS helps analyze terrain, soil conditions, and environmental risks before construction begins.
- Urban Planning: It aids in planning large-scale projects by visualizing how buildings fit within the broader cityscape.
- Geospatial Integration: Using tools like ArcGIS GeoBIM, users can link geospatial and BIM datasets, enabling seamless collaboration.
ArcGIS is particularly useful in projects involving:
- Infrastructure planning (roads, bridges).
- Disaster resilience modeling.
- Environmental impact assessments.
ArcGIS enriches BIM workflows by expanding the data inputs beyond the structure to include its surroundings, offering a holistic view of a project’s impact and feasibility.
Key Differences Between ArcGIS and BIM Tools Like Revit or AutoCAD
Understanding the distinctions between ArcGIS and BIM tools clarifies their respective roles in the AEC ecosystem:
- Primary Use Cases:
- ArcGIS is ideal for spatial analysis, mapping, and environmental planning.
- BIM software excels at detailed building design and lifecycle management.
- Technical Capabilities:
- ArcGIS handles geospatial datasets and integrates them with environmental factors.
- BIM tools focus on precise building specifications, such as material quantities and structural integrity.
- Output:
- ArcGIS provides maps, spatial models, and geographic visualizations.
- BIM software outputs include detailed 3D building models and construction-ready documentation.
While ArcGIS cannot fully replace a BIM tool, it fills a crucial gap by adding a geospatial dimension to BIM workflows, enabling a more comprehensive analysis of projects.
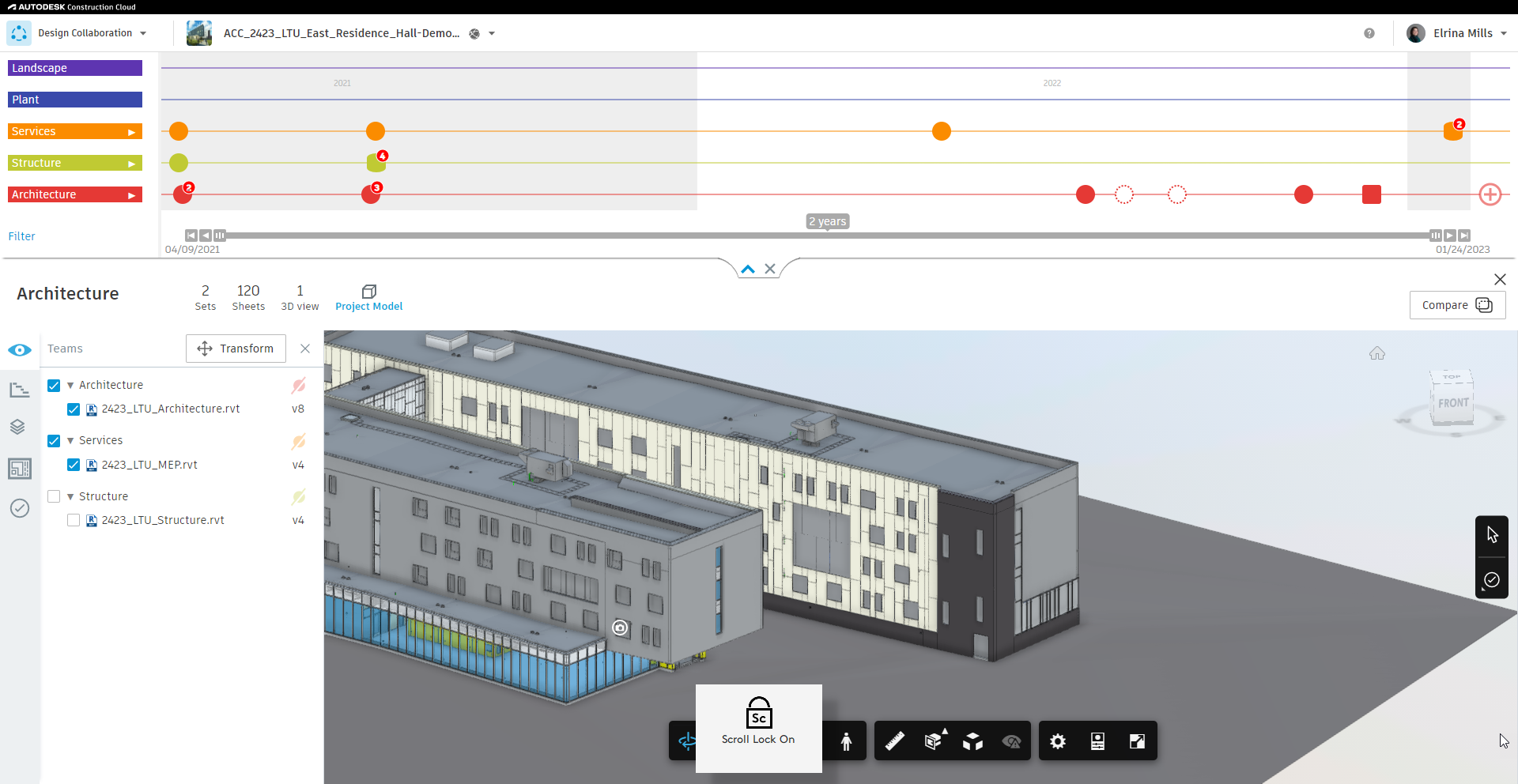
How ArcGIS and BIM Work Together
Integration of ArcGIS with BIM Platforms
The integration of ArcGIS with BIM platforms unlocks new possibilities for managing complex projects, especially those involving urban planning and large-scale infrastructure development. Tools like ArcGIS GeoBIM, developed by Esri, are specifically designed to connect geospatial data from ArcGIS with BIM data from platforms like Autodesk Revit and Navisworks.
Key benefits of this integration include:
- Seamless Data Sharing: ArcGIS allows geospatial data (like terrain, zoning information, or flood risk areas) to be shared directly with BIM models, ensuring that designers have complete contextual information.
- Enhanced Visualization: By overlaying BIM models onto GIS maps, stakeholders can visualize projects in real-world environments, helping to identify potential issues early.
- Improved Collaboration: ArcGIS and BIM integration fosters communication across teams by offering a unified platform for viewing and analyzing geospatial and building data.
How It Works:
ArcGIS GeoBIM uses cloud-based tools to connect GIS and BIM data. For instance, it can overlay a 3D building model from Revit onto a GIS map, allowing users to assess how the structure fits within its geographic context. This integration enables tasks such as environmental impact analysis, site optimization, and infrastructure planning to be executed more effectively.
Real-World Applications of ArcGIS and BIM Integration
The combination of ArcGIS and BIM has been successfully applied in various industries, creating smarter workflows and better project outcomes. Here are some notable use cases:
- Urban Development:
In large cities, integrating ArcGIS and BIM helps urban planners visualize how new developments interact with existing infrastructure. For example, a city planning department could use the combined tools to evaluate traffic flow or the impact of new construction on flood-prone areas. - Smart City Initiatives:
Many smart city projects rely on GIS and BIM integration to create digital twins—virtual replicas of urban environments. ArcGIS provides the geospatial layer, while BIM contributes the structural and design details. - Disaster Preparedness and Resilience:
In regions prone to natural disasters, ArcGIS and BIM integration is used to simulate disaster scenarios and develop resilient infrastructure. For example, a flood-prone city might model how rising water levels could impact roads, bridges, and buildings. - Transportation Infrastructure:
The combination of GIS and BIM is invaluable in designing and managing transportation systems, such as highways, railways, and airports. Engineers use ArcGIS to analyze topographical challenges and integrate those insights into BIM models for construction.
Case Study Example:
A prominent application of ArcGIS and BIM integration was seen in the design of a major urban transportation hub. By combining ArcGIS’s spatial analysis with BIM’s detailed structural models, the project team was able to optimize the station’s design to account for passenger flow, environmental impact, and geographic constraints. This collaboration reduced costs and improved operational efficiency.
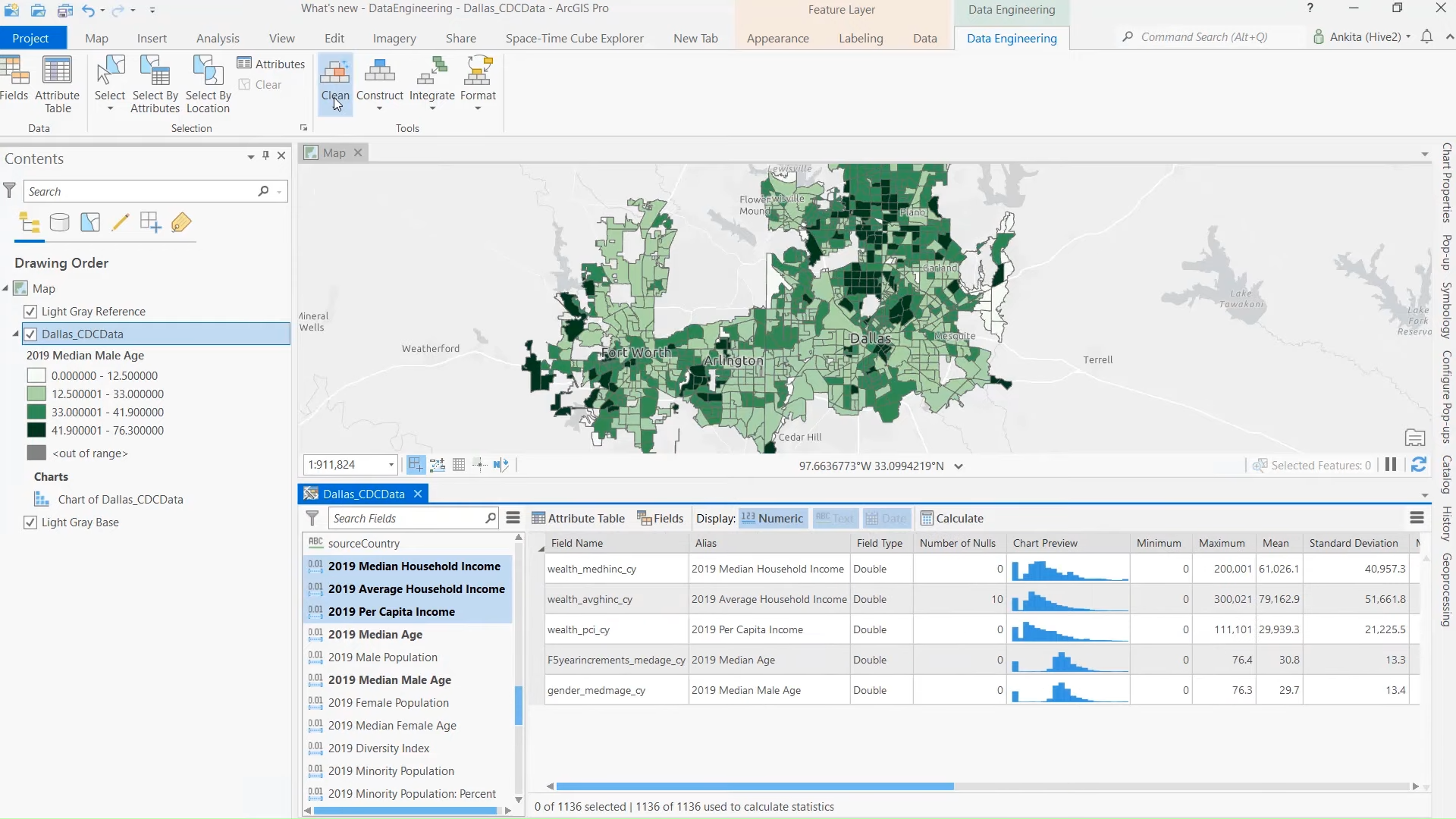
Advantages of Using ArcGIS in BIM Processes
Enhanced Spatial Context
One of the greatest advantages of using ArcGIS in BIM workflows is the ability to provide geospatial context to building designs and infrastructure projects. BIM tools are excellent for creating detailed models of structures, but they often lack the ability to incorporate the surrounding environmental factors effectively. ArcGIS fills this gap by integrating geographic data such as:
- Topography and elevation models.
- Land use and zoning information.
- Proximity to natural resources or environmental hazards.
For example, when designing a new housing complex, ArcGIS can analyze the site’s terrain to ensure optimal placement of buildings, roads, and drainage systems. This reduces construction risks and helps create designs that are in harmony with their natural surroundings.
Improved Decision-Making
ArcGIS enhances the decision-making process by enabling comprehensive site analysis and risk assessment. It allows project stakeholders to consider external factors that may affect construction, such as:
- Flood Risk Zones: Identify areas prone to flooding and adjust designs accordingly.
- Seismic Activity: Map out earthquake-prone regions to improve structural safety.
- Environmental Impact: Evaluate how construction could affect local ecosystems.
By layering this critical data onto BIM models, ArcGIS helps decision-makers choose sites, designs, and materials that align with environmental and regulatory requirements. This leads to smarter, more sustainable projects.
Streamlined Collaboration
Collaboration in AEC projects often involves multiple stakeholders, from architects and engineers to city planners and environmental consultants. Integrating ArcGIS with BIM streamlines this collaboration by providing a unified platform where all parties can access and interact with the same datasets.
Key benefits include:
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Cloud-based tools like ArcGIS GeoBIM enable teams to update and share information in real time.
- Cross-Disciplinary Insights: Geospatial data from ArcGIS complements structural data from BIM, offering a complete picture that fosters better communication between diverse teams.
- Improved Stakeholder Engagement: Visualizing BIM models in a geospatial context makes it easier for non-technical stakeholders to understand project implications.
Driving Cost and Time Efficiency
By combining ArcGIS and BIM, project teams can achieve significant cost and time savings. This is possible through:
- Early Problem Detection: Identifying geographical challenges, such as unstable terrain or zoning restrictions, during the design phase prevents costly redesigns or delays.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: ArcGIS allows precise mapping of resources, ensuring that construction materials, labor, and equipment are deployed efficiently.
- Minimized Environmental Risks: Avoiding sensitive areas or hazardous zones helps projects stay on schedule and avoid fines or remediation costs.
Example: A study conducted on infrastructure projects showed that integrating GIS and BIM reduced project delays by 25% and saved up to 15% on costs related to site planning and risk mitigation.